The Violet Gazette
 |
Return to AVS Homepage
Return to The Violet Gazette Index
Return to The Summer 2000 Contents
Published by THE AMERICAN VIOLET SOCIETY
Written by: Scott D. Appell.
© 2000 All Rights Reserved.
Volume 1, Number 3
Summer 2000
On line Version
PAGE 4
The
Ethnobotanical Uses of the
Genus Viola by Native Americans
|
 |
|
|
Scott D. Appell is currently Director of Education for the
Horticultural Society of New York, a member of the Publications
Committee of the Pennsylvania Horticultural Society and a Board Member
of The American Violet Society. He is a contributing editor to Smith
& Hawken's Book of Outdoor Gardening and Rodale Press' 1001
Ingenious Gardening Ideas as well as botanical consultant for Gardens by
the Sea: Creating a Tropical Paradise, published by The Garden Club of
Palm Beach. He has written three books: Pansies, Lilies and Tulips, all
published by Friedman/Fairfax Publishers, Inc. (New York). His latest
work, Orchids (also published by Friedman/Fairfax) is slated for winter
2001. In addition, he is guest editor/writer for Landscaping Indoors:
Bringing the Outdoors, a part of the 21st-Century Gardening Series
handbooks published by the Brooklyn Botanic Garden, also slated for
winter 2001. Scott Appell lives, writes and teaches horticulture in New
York City . His private horticultural consultation company is called The
Green Man,
|
|
|
We admire them flowering in cultivated gardens, fields and glades
or abandoned farm steads. We view their images incorporated into the
Medieval Unicorn tapestries hung in the Cloisters or Cluny Museums. We
hear them mentioned in theatrical performances ranging from
Shakespeare's Hamlet, King John, Twelfth Night, Midsummer Night's Dream
and Cymbeline to Lerner and Loewe's My Fair Lady. We even partake of
them al fresco in fashionable tidbits or candied upon lavish
confections. They are the violets, the genus Viola. Although we are all
well aware of violets in these various guises, few of us are cognizant
of their ethnobotanical (i.e. medicinal, nutritional and folkloric) uses
among our Native Americans. We will review both indigenous and
introduced species of violets. Whether we refer to our various neolithic
emigrant populace as Native Americans, First Americans, American Indians
or simply Indians, is a very personal matter, indeed, bogged down by
intense political, moral and etymological parameters. In this simple
report I will utilize the tribal appellations.
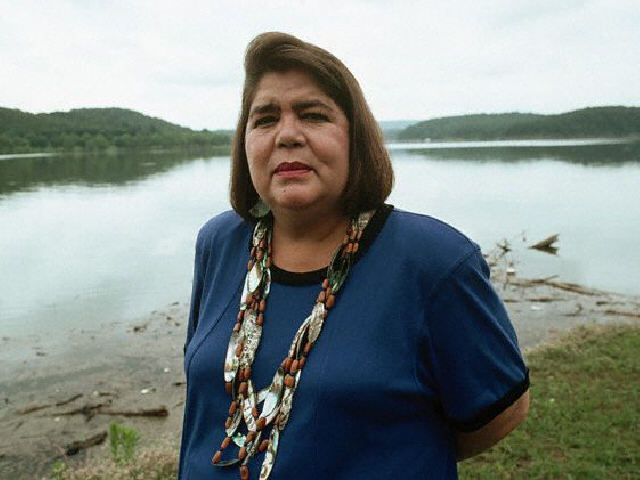 |
Chief
Wilma Mankiller,
First Woman Leader of the Cherokee Nation |
Key to The People
As you peruse this elementary format, notice how so many different
species of Viola are used for the exact same purpose by different tribes
of First Americans. Here is a brief description of the various tribes I
refer to:
| Blackfoot. |
The Blackfoot hunted over the region of Montana, Alberta
and Saskatchewan. Blackfoot is a common spelling in Canada, whereas
Blackfeet is more common in the United States. |
| Carrier |
Southern. Near Ulkatcho, in northwestern British
Columbia. |
| Cherokee |
The Cherokees are found throughout most of western North
Carolina, and in northwestern Georgia. |
| Diegueno |
The Diegueno live throughout southernmost California. |
| Eskimo, Inukitut |
Alaska, Canada and Greenland. |
| Klallam |
Southern shore of Vancouver Island, British Columbia,
and the northern central Olympic Peninsula, Washington. |
| Iroquois |
The Iroquois live throughout upstate New York and in
southern Quebec. |
| Luiseno |
Southern California, near San Juan Capistrano. |
| Makah |
Northwestern tip of the Olympic Peninsula, Washington. |
| Navaho, Ramah |
Western New Mexico. |
| Ojibwa |
Also known as Chippewa, Ojibwas are located in the upper
Midwest and Southern Ontario. |
| Ojibwa |
South Red Lake and Leech Lake Minnesota |
| Tanana |
Upper. Alaska, between Anchorage and Fairbanks. |
| Tolowa |
Northwestern California. |
 |
| Blackfoot
on Horseback |
Glossary of Uses
| Decoction |
A preparation made by simmering a botanical in water for
an extended period of time. |
| Emetic |
An agent which induces
vomiting. |
| Infusion |
An extract of some
botanical derived from soaking it briefly in water. |
| Poultice |
Material applied to the
surface of the body as a remedy for some disorder. |
THE VIOLETS
Viola adunca,
the Hookedspur Violet
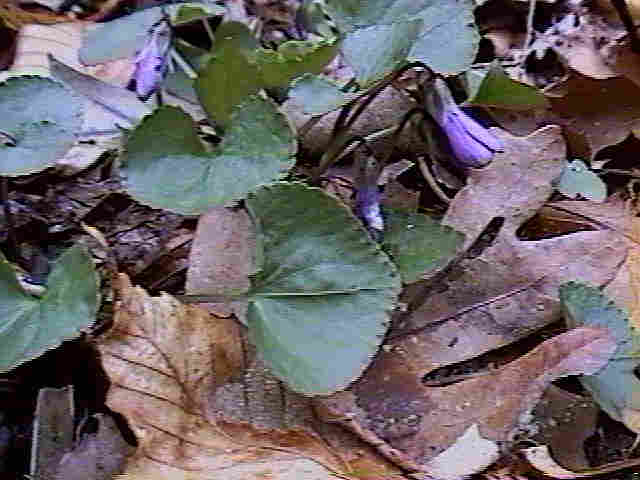 |
| Viola
adunca |
Medicinal
Uses
Blackfoot
| External
Antirheumatic: |
Infusion
of the roots and leaves applied to
sore and swollen joints. |
| Pediatric
Aid and Respiratory Aid: |
Infusion
of leaves and roots given to asthmatic
children. |
|
Carrier,
Southern
Analgesic
and
Gastrointestinal Aid: |
Decoction
of entire plant taken for stomach
pain. |
|
Klallam
| Analgesic: |
Poultice of smashed flowers applied to the chest for pain. |
|
Makah
| Gynecological Aid: |
Roots and leaves chewed by women during labor.
. |
|
Tolowa
| Eye Medicine: |
Poultice of chewed leaves applied to sore eyes. |
|
|
As
a Dye Plant
Blackfoot
| Blue: |
Plant used to dye arrows
blue |
|
|
|
|
Viola
bicolor, the Johnny-Jump-Up
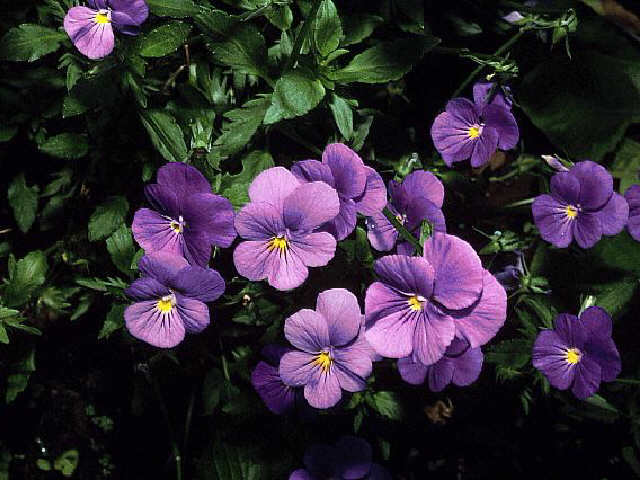 |
| Johnny
Jumpups |
Medicinal
Uses
Cherokee
| Analgesic: |
Poultice
of leaves used for headache. |
| Antidiarrheal: |
Infusion taken for
dysentery. |
| Blood Medicine: |
Infusion taken for blood. |
| Cold Remedy: |
Infusion taken for colds. |
| Cough Medicine: |
Infusion with sugar taken for
coughs. |
| Dermatological Aid: |
Poultice of crushed roots applied to boils. |
|
Respiratory Aid: |
Infusion sprayed up nose for catarrh. |
| Tonic: |
Infusion
taken as spring tonic. |
|
|
Agricultural Uses
Cherokee
| Insecticide: |
Infusion
of roots used to soak corn seeds prior to planting to repel insects. |
|
|
|
|
Viola biflora, the Two Flower Violet
Miscellaneous Uses
Eskimo,
Inukitut
|
Incense and Fragrance: |
Stems with flowers placed among clothes. |
|
|
|
|
Viola blanda, the Sweet White Violet
Food
Cherokee
| Vegetable: |
Leaves and
stems mixed with other greens, parboiled, rinsed, and fried in fat with
salt until soft. |
|
|
|
|
Viola canadensis, the Canadian White
Violet
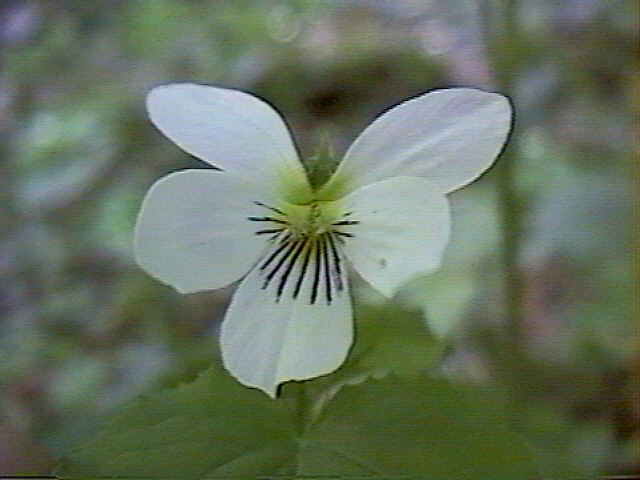 |
| Canadian
Violet |
Medicinal
Uses
Ojibwa,
South
| Analgesic: |
Decoction of roots used for pains of or
near the bladder. |
|
|
|
|
Viola conspersa, the American Dog Violet
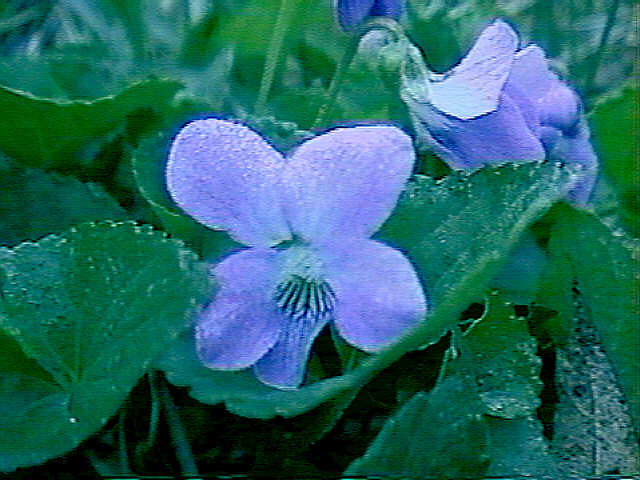 |
| American
Dog Violet (Viola conspersa) |
Medicinal
Uses
Ojibwa
| Heart Medicine: |
Infusion of the whole plant taken for heart
trouble |
|
|
|
|
Viola cucullata, the Blue Marsh Violet
 |
| Blue
Marsh Violet (Viola cucullata) |
Medicinal
Uses
Cherokee
| Analgesic: |
Poultice of leaves used for headache. |
| Antidiarrheal: |
Infusion taken for dysentery. |
| Blood Medicine: |
Infusion taken for blood. |
|
Cold Remedy: |
Infusion taken for colds. |
| Cough Medicine: |
Sweetened
infusion taken for coughs. |
| Dermatological Aid: |
Poultice of crushed roots
applied to boils. |
| Respiratory Aid: |
Infusion sprayed up nose for catarrh. |
|
Tonic: |
Infusion taken as spring tonic. |
|
|
|
|
Viola epipsila, the Dwarf Marsh
Violet
Miscellaneous Uses
Tanana,
Upper
|
Incense and Fragrance: |
Dried
roots used as incense in potlatches. |
|
|
|
|
Viola nephrophylla, the Northern
Bog Violet
Medicinal
Uses
Navajo,
Ramah
| Ceremonial Medicine and Emetic: |
Plant used as ceremonial emetic. |
|
|
|
|
Viola pedata, the Bird's foot Violet
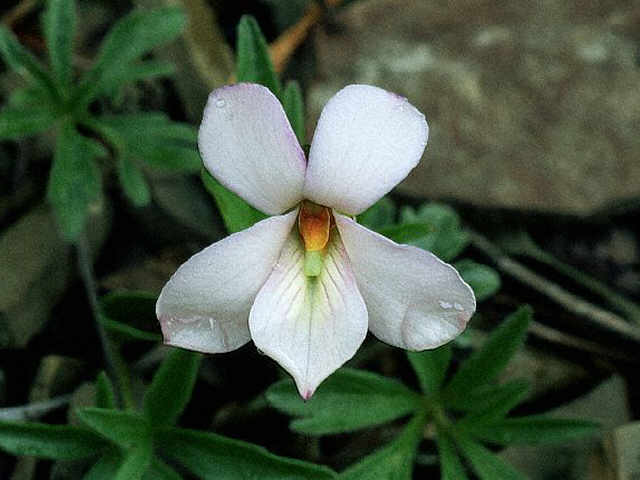 |
| White
Birdsfoot Violet (Viola pedata) |
Medicinal
Uses
Cherokee
| Analgesic: |
Poultice of leaves used for headache. |
| Antidiarrheal: |
Infusion taken for dysentery. |
| Blood Medicine: |
Infusion taken for blood. |
|
Cold Remedy: |
Infusion taken for colds. |
| Cough Medicine: |
Sweetened
infusion taken for coughs. |
| Dermatological Aid: |
Poultice of crushed roots
applied to boils. |
| Respiratory Aid: |
Infusion sprayed up nose for catarrh. |
|
Tonic: |
Infusion taken as spring tonic. |
|
|
Agricultural
Uses
Cherokee
| Insecticide: |
Infusion of roots used to soak
corn seeds prior to planting to repel insects. |
|
|
|
|
Viola
pedunculata, the
California Golden Violet
Food
Diegueno
| Vegetable: |
Young
leaves, picked before flowers appear
are boiled once, and eaten as green. |
|
Luiseno
| Vegetable: |
Leaves used as greens. |
|
|
|
|
Viola pubescens var. pubescens, the
Smooth Yellow Violet
 |
| Smooth
Yellow Violet (Viola pubescens) |
Medicinal
Uses
Iroquois
| Gastrointestinal Aid: |
Compound decoction of plants taken for indigestion. |
|
|
Food
Cherokee
| Vegetable: |
Leaves and stems mixed with other greens, parboiled. Then
fried in fat with salt until tender. |
|
|
|
|
Viola sagittata, the Arrowleaf
Violet
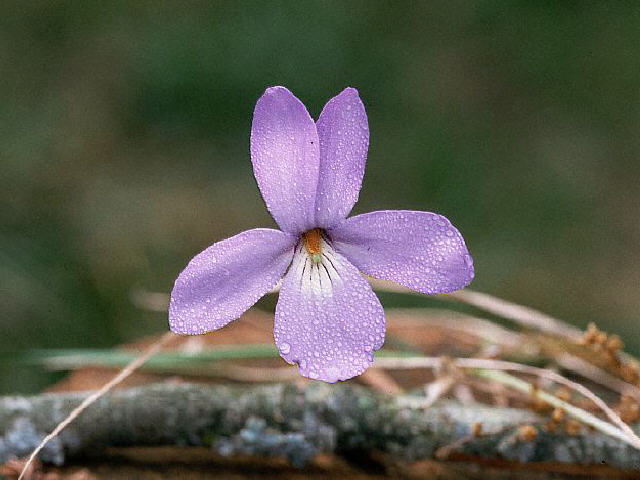 |
| Arrow
Leaved Violet |
Medicinal
Uses
Iroquois
| Witchcraft
Medicine: |
Compound
used to detect bewitchment. |
|
|
|
|
Viola striata, the Striped Cream Violet
 |
| Striped
Creamy Violet (Viola striata) |
Medicinal
Uses
Iroquois
| Witchcraft
Medicine: |
Plant used to make a girl sick and
crazy by her rejected suitor after he has been refused by her parents. ? |
|
|
|
|
© 2000 Scott D. Appel
For The American Violet Society
All Rights Reserved
|
|
|